Grade 8 Science : Food Preservation - Part 2

We have already learnt that food preservation involves in controlling the factors that affect food spoilage in order to make food last longer through artificial techniques/methods. Many measures like the prevention of the entry of microbes in to food, controlling the water content, controlling the temperature of food and prevention of damage that results from the activity of microbes can be followed in the process of preserving food.
Food preservation had been followed since past where plenty of fruits and vegetables were grown by Sri Lankans and the excess was preserved. There are several traditional methods of food preservation.
- - Drying - Examples : Jackfruit, Breadfruit, Chilies, Green gram, Paddy, Spices
- - Smoking – Examples : Meat, Fish, Garcenia
- - Immersing in bee honey – Examples : Dry meat
- - Salting – Examples: Mango, Fish (Dried fish/”Karawala”, Lime (“Lunu dehi”)
- - Keeping under dry sand – Examples : Jack seeds (“wali kos”) , Ginger, Lime, Potatoes
With the advancement of technology, food preservation methods have evolved to a greater extent.
- - Drying – Examples : Drying by sun’s heat (solar heat driers), Stove drying, Spray Drying
- - Temperature Control – Examples : Freezing, Deep Freezing
- - Concentration – Examples : Canning, Bottling
In the solar heat driers, food is dried using the heat rays of the sun. It is more convenient to obtain cleaner and dry food free from wastes and damages by rain/ animals in a short lapse of time due to the availability of a closed condition in the drier. (Examples: Fruits, Vegetables, Chilies.) Stove drying allows to provide suitable temperature for the food and it uses gas, electricity and mineral oil to operate (Examples: Mushrooms, Chilies, Fruits). Spray Drying occurs especially in the production of powdered forms of food. For example, in the production of milk powder, hot milk is sprayed onto a heated cylinder with high pressure. Thus, the water content inherent in milk is removed where the microbial growth is prevented.
We learnt that microbial growth requires a favorable temperature and by reducing it to a value that does not support their existence, it can be controlled. Freezing is one way of controlling the temperature in food. Here, the temperature of food can be maintained lower than the room / normal temperature. The temperature of the normal freezing chambers must be below 4 0C. (Examples: fruits, vegetables, dairy products like butter). The temperature of deep freezers should be below -180C and it can prevent the growth of many microbes. This is quite efficient is preserving the properties of food like the nutrient values, taste, appearance, texture and etc. (Examples: Meat, Fish, Ice Cream).
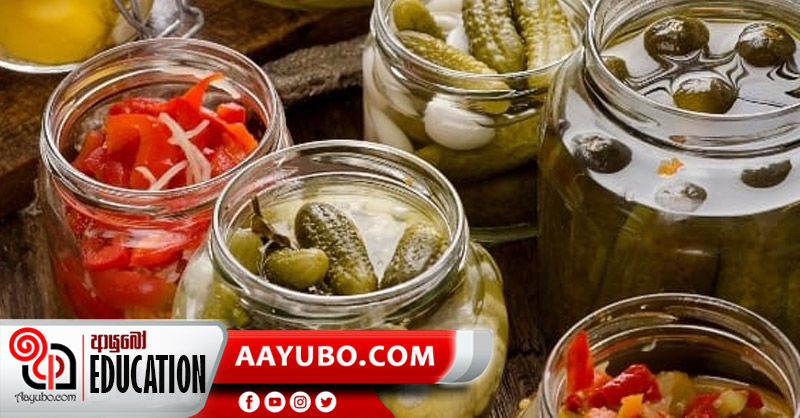
Concentration involves in techniques like canning and bottling. Here, the water and air content in food is removed and this controls microbial growth. The food is packed into glass jars and following this, the jars are heated. This forms a vacuum seal that will suppress the microbial growth. Several preservatives are also added to prevent the microbial activity further. Examples: (Bottling – Cordial, Jam), (Canning - Fruits, Sweet Corn, Fish).
by Mekhala Egodawele
Photo source : Internet
915 Views







Comments